Vue Router
一、前端路由与后端路由
后端路由:
服务器将浏览器请求的url解析之后映射对应的函数,该函数根据资源类型的不同进行不同操作。,若是静态资源,则进行文件的读取,若是动态数据,就会通过数据库进行一些增删查改的操作。
前端路由:
随着前端单页应用(SPA)的兴起,前端页面完全变成了组件化,不同的页面就是不同的组件,页面的切换就是组件的切换;页面切换的时候不需要再通过http请求,直接通过JS解析url地址,然后找到对应的组件进行渲染。
两者区别:
前端路由与后端路由最大的不同就是不需要再经过服务器,直接在浏览器下通过 JS 解析页面之后就可以拿到相应的页面。
各自的优缺点:
后端路由的优点是利于SEO且安全性较高;缺点就是代码耦合度高,加大了服务器压力,且 http 请求受限于网络环境,影响用户体验。
前端路由的优点就是组件切换不需要发送 http 请求,切换跳转快,用户体验好;缺点就是没有合理的利用缓存且不利于SEO。
二、单页面前端路由模式
vue-router 在实现单页面前端路由时,提供了三种方式:Hash 模式、History 模式、abstract 模式,根据 mode 参数来决定采用哪一种方式.
hash 模式
vue-router的默认模式。- 使用
URL的hash来模拟一个完整的URL,当URL改变时,页面不会去重新加载。 hash(#)是URL的锚点,代表的是网页中的一个位置,单单改变#后的部分(/#/..),浏览器只会加载相应位置的内容,不会重新加载网页,也就是说 #是用来指导浏览器动作的,对服务器端完全无用,HTTP请求中不包括#;同时每一次改变#后的部分,都会在浏览器的访问历史中增加一个记录,使用”后退”按钮,就可以回到上一个位置;所以说 Hash 模式通过锚点值的改变,根据不同的值,渲染指定DOM位置的不同数据。- 通过
window.location.hash获取到当前 url 的 hash;hash 模式下通过hashchange方法可以监听 url 中 hash 的变化
js
window.addEventListener('hashchange', function () {}, false);
window.addEventListener('hashchange', function () {}, false);
hash 模式优缺点
hash模式的特点是兼容性更好,并且hash的变化会在浏览器的history中增加一条记录,可以实现浏览器的前进和后退功能;缺点由于多了一个#,所以url整体上不够美观。
history 模式
history模式是另一种前端路由模式,它基于HTML5的history对象- 通过
location.pathname获取到当前 url 的路由地址;history模式下,通过pushState和replaceState方法可以修改url地址,结合popstate方法监听url中路由的变化
history 模式优缺点
history模式的特点是实现更加方便,可读性更强,同时因为没有了#,url也更加美观。- 这种模式要玩好,还需要后台配置支持。如果 URL 匹配不到任何静态资源,则应该返回同一个
index.html页面,这个页面就是app依赖的页面(即将路由都重定向到根路由)。
abstract 模式
abstract模式是使用一个不依赖于浏览器的浏览历史虚拟管理后端。- 根据平台差异可以看出,在
Weex环境中只支持使用abstract模式。 不过,vue-router自身会对环境做校验,如果发现没有浏览器的API,vue-router会自动强制进入abstract模式,所以 在使用vue-router时只要不写 mode 配置即可,默认会在浏览器环境中使用hash模式,在移动端原生环境中使用abstract模式。 (当然,你也可以明确指定在所有情况下都使用abstract模式)
三、vue-router 工作流程
- url 改变
- 触发事件监听
- 改变 vue-router 中的 current 变量
- 监视 current 变量的监视者
- 获取新的组件
- render
Vue.use()
Vue.use()方法用于插件安装,通过它可以将一些功能或 API 入侵到 Vue 内部;- 它接收一个参数,如果这个参数有 install 方法,那么
Vue.use()会执行这个install方法,如果接收到的参数是一个函数,那么这个函数会作为install方法被执行 install方法在执行的时候也会接收到一个参数,这个参数就是当前 Vue 的实例- 通过接收到的
Vue实例,可以定义一些全局方法或属性,也可以通过prototype对Vue的实例方法进行扩展
js
class vueRouter {
constructor() {}
}
vueRouter.install = function (Vue) {};
class vueRouter {
constructor() {}
}
vueRouter.install = function (Vue) {};
Vue.mixin()
Vue.mixin()方法用于注册全局混入,它接收一个对象作为参数,我们将这个对象称为混入对象;混入对象可以包含组件的任意选项;通过混入对象定义的属性和方法在每一个组件中都可以访问到.
js
<!-- router.js -->
class vueRouter {
constructor(){
}
}
vueRouter.install = function(Vue) {
Vue.mixin({
data(){
return {
name: '阿白smile'
}
}
})
}
<!-- home.vue -->
// 省略代码
<script>
export default {
created(){
console.log(name) // '阿白smile'
}
}
</script>
<!-- router.js -->
class vueRouter {
constructor(){
}
}
vueRouter.install = function(Vue) {
Vue.mixin({
data(){
return {
name: '阿白smile'
}
}
})
}
<!-- home.vue -->
// 省略代码
<script>
export default {
created(){
console.log(name) // '阿白smile'
}
}
</script>
四、实现一个 routerJs
- 在
router.js中
js
// 1. 注册路由插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2. 路由规则
...
// 3. 创建 router 对象
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'hash',
// mode: 'history',
routes
})
// 导出router 对象
export default router
// 1. 注册路由插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2. 路由规则
...
// 3. 创建 router 对象
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'hash',
// mode: 'history',
routes
})
// 导出router 对象
export default router
- 编写
vuerouter.js
js
let _Vue = null;
export default class VueRouter {
// 实现install方法,通过install向全局注入vueRouter
static install(Vue) {
// 1、判断当前插件是否已经被安装
if (VueRouter.install.installed) {
return;
}
VueRouter.install.installed = true;
// 2、把 Vue 构造函数记录到全局变量
_Vue = Vue;
// 3、把创建 Vue 实例的时候传入的 router 对象注入 Vue 实例上
// 混入
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.router) {
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router;
this.$options.router.init();
}
},
});
}
constructor(options) {
this.options = options;
this.mode = options.mode || 'hash';
this.routeMap = {};
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current: '/',
});
}
init() {
this.createRouteMap();
this.initComponents(_Vue);
this.initCurrent();
this.initEvents();
}
createRouteMap() {
// 遍历所有的路由规则,把路由规则解析成键值对的形式,储存到 routeMap 中
this.options.routes.forEach((route) => {
this.routeMap[route.path] = route.component;
});
}
initComponents(Vue) {
const Link = {
name: 'RouterLink',
props: {
to: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
},
methods: {},
};
if (this.mode === 'history') {
Link.render = function (h) {
return h(
'a',
{
attrs: {
href: this.to,
},
on: {
click: this.clickHandler,
},
},
this.$slots.default
);
};
Link.methods.clickHandler = function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
history.pushState({}, '', this.to);
this.$router.data.current = this.to;
};
} else {
Link.render = function (h) {
return h(
'a',
{
attrs: {
href: '/#' + this.to,
},
},
this.$slots.default
);
};
}
const View = {
render: (h) => h(this.routeMap[this.data.current]),
};
Vue.component('router-link', Link);
Vue.component('router-view', View);
}
// 第一次加载页面初始化
initCurrent() {
// history模式
if (this.mode === 'history') {
this.data.current = location.pathname;
return;
}
// hash模式
if (location.hash === '') {
window.location.hash = '#/';
}
this.data.current = location.hash.slice(1);
}
initEvents() {
// 监听hash改变
window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => {
this.data.current = location.hash.slice(1);
});
// 监听浏览器的的历史记录 当历史记录条目更改时,将触发popstate事件
window.addEventListener('popstate', () => {
this.data.current = window.location.pathname;
});
}
}
let _Vue = null;
export default class VueRouter {
// 实现install方法,通过install向全局注入vueRouter
static install(Vue) {
// 1、判断当前插件是否已经被安装
if (VueRouter.install.installed) {
return;
}
VueRouter.install.installed = true;
// 2、把 Vue 构造函数记录到全局变量
_Vue = Vue;
// 3、把创建 Vue 实例的时候传入的 router 对象注入 Vue 实例上
// 混入
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.router) {
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router;
this.$options.router.init();
}
},
});
}
constructor(options) {
this.options = options;
this.mode = options.mode || 'hash';
this.routeMap = {};
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current: '/',
});
}
init() {
this.createRouteMap();
this.initComponents(_Vue);
this.initCurrent();
this.initEvents();
}
createRouteMap() {
// 遍历所有的路由规则,把路由规则解析成键值对的形式,储存到 routeMap 中
this.options.routes.forEach((route) => {
this.routeMap[route.path] = route.component;
});
}
initComponents(Vue) {
const Link = {
name: 'RouterLink',
props: {
to: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
},
methods: {},
};
if (this.mode === 'history') {
Link.render = function (h) {
return h(
'a',
{
attrs: {
href: this.to,
},
on: {
click: this.clickHandler,
},
},
this.$slots.default
);
};
Link.methods.clickHandler = function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
history.pushState({}, '', this.to);
this.$router.data.current = this.to;
};
} else {
Link.render = function (h) {
return h(
'a',
{
attrs: {
href: '/#' + this.to,
},
},
this.$slots.default
);
};
}
const View = {
render: (h) => h(this.routeMap[this.data.current]),
};
Vue.component('router-link', Link);
Vue.component('router-view', View);
}
// 第一次加载页面初始化
initCurrent() {
// history模式
if (this.mode === 'history') {
this.data.current = location.pathname;
return;
}
// hash模式
if (location.hash === '') {
window.location.hash = '#/';
}
this.data.current = location.hash.slice(1);
}
initEvents() {
// 监听hash改变
window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => {
this.data.current = location.hash.slice(1);
});
// 监听浏览器的的历史记录 当历史记录条目更改时,将触发popstate事件
window.addEventListener('popstate', () => {
this.data.current = window.location.pathname;
});
}
}
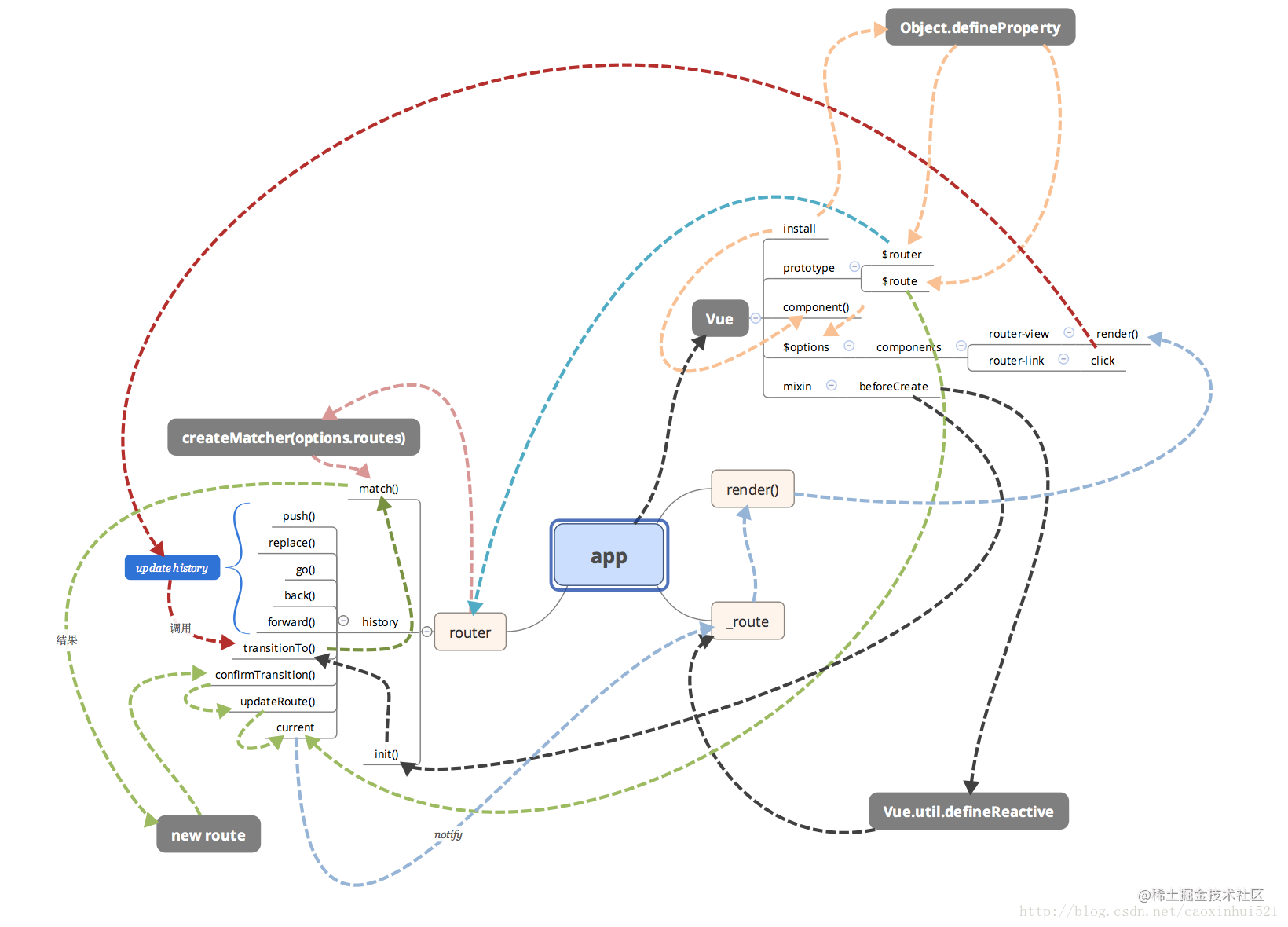
附录:vue-router 源码图解
 Attraction11
Attraction11