Redux 介绍
Redux vs MobX vs Recoil 对比
- Redux集中管理一个大状态,优点是比较专一,缺点是对于某些场景,比如不需要大量共享状态的时候,就不是特别灵活。
- MobX和Recoil是可以分散式管理状态,因此相对Redux来说,状态比较单一来源。MobX主要实现思路是拦截状态值的get与set函数,get时候的把状态值标记可观察变量,set的时候让组件更新。
- Recoil由于又多了一层selector,因此又可以渐进式定义状态。因此,就学习成本来说,一般是这样:Redux < MobX < Recoil。
目前国内来看,Redux的使用率是高于MobX的,比如Umi/DVA底层就是Redux。Recoil到现在一直没发正式版,主要是用在Facebook内部比较多。
安装
npm install redux --save
npm install --save react-redux
npm install --save-dev redux-devtools
npm install --save react-redux
npm install --save-dev redux-devtools
Redux 工作流程
Redux基于函数式编程思想实现,集中式管理状态:
- 单一数据源: 整个应用的 全局 state 被储存在一棵 object tree 中,并且这个 object tree 只存在于唯一一个 store 中。
- State 是只读的: 唯一改变 state 的方法就是触发 action,action 是一个用于描述已发生事件的普通对象。
- 使用纯函数来执行修改: 为了描述 action 如何改变 state tree,你需要编写纯的 reducers。
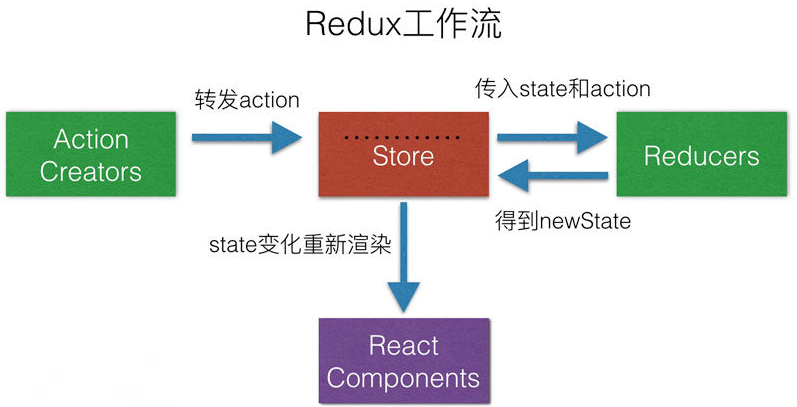
在 React Components 中派发dispatch 出 Action,Store 会自动调用 Reducers 去修改 State 状态后将新的 State 交给 Store。 State 发生变化后重新渲染。
Redux 三个核心概念
Action
动作对象,包含两个属性(type 标识属性,值为字符串、data 数据属性,值类型任意)
{type: 'ADD_STUDENT', data: {name: 'Tom', age: 20}}
Store
状态数据仓库,强调一下 Redux 应用只有一个单一的 store
Store 有以下职责:
- 维持应用的 state;
- 提供
getState()方法获取 state; - 提供
dispatch(action)方法更新 state; - 通过
subscribe(listener)注册监听器; - 通过
replaceReducer(nextReducer)返回的函数注销监听器。
Reducers
是个函数通过获取动作改变 State 状态,生成个新的 State 状态
注意:Reducers 只负责修改数据状态,不负责重新更新渲染页面
Redux 编写流程
创建 Store
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import Reducer from './Reducer';
const store = createStore(Reducer);
export default store;
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import Reducer from './Reducer';
const store = createStore(Reducer);
export default store;
创建纯函数 Reducer
// Reducer.js
const defaultState = {} // 初始化默认值State
export default const Reducer = (previousState = defaultState, action) => {
const {type, data} = action
// 根据不同的Action Type返回不同的State
return newState
}
// Reducer.js
const defaultState = {} // 初始化默认值State
export default const Reducer = (previousState = defaultState, action) => {
const {type, data} = action
// 根据不同的Action Type返回不同的State
return newState
}
组件中获取 Store 的状态数据
在组件中通过 store.getState() 获取数据
组件中修改 Store 的状态数据
在组件调用 store.dispatch({type: '', data: {}}) 方法去执行 Reducer
dispatch派发
状态数据发生变化后,更新页面
通过 store.subscribe(callback) 方法,在数据发送变化后,执行回调
subscribe订阅
componentDidMount(){
//检测Redux中状态的变化,只要变化就更新页面变化
store.subscribe(()=>{
this.setState({})
})
}
componentDidMount(){
//检测Redux中状态的变化,只要变化就更新页面变化
store.subscribe(()=>{
this.setState({})
})
}
Redux DevTools 调试插件
- 在谷歌浏览器下载 Redux DevTools 插件
- 配置 Redux DevTools 插件
// 只需要要 创建 store 仓库添加下面一条代码,就是最简单的配置
// 3. 创建 store 仓库
const store = createStore(
reducer,
++window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ &&
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);
// window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
// 只需要要 创建 store 仓库添加下面一条代码,就是最简单的配置
// 3. 创建 store 仓库
const store = createStore(
reducer,
++window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ &&
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);
// window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
写 Redux 的小技巧
把 Action types 单独 写入一个文件
写
Redux Action的时候,我们写了很多 Action 的派发,产生了很多Action Types,如果需要Action的地方我们就自己命名一个Type,会出现两个基本问题:
- 这些 Types 如果不统一管理,不利于大型项目的服用,设置会长生冗余代码。
- 因为
Action里的Type,一定要和Reducer里的type一一对应在,所以这部分代码或字母写错后,浏览器里并没有明确的报错,这给调试带来了极大的困难。
建议把 Action Type 拆分出来, 把 type 变量名 放在一个文件统一管理
// 例子:
export const TYPE_1 = 'type1';
export const TYPE_2 = 'type2';
export const TYPE_3 = 'type3';
// 例子:
export const TYPE_1 = 'type1';
export const TYPE_2 = 'type2';
export const TYPE_3 = 'type3';
把 Action 也单独写入一个文件
组件里有很多 Action,并且分散才程序的各个地方,如果庞大的工程,这势必会造成严重的混乱
拿自己的 todo 案例:
// 在组件引入
import {changeInputAction, addItemAction, deleteItemAction} from './store/actionCreators'
changeInputValue(e) {
// 实时获取输入框内容 e.target.value
const action = changeInputAction(e.target.value)
store.dispatch(action)
}
storeChange() {
this.setState(store.getState())
}
clickBtn() {
const action = addItemAction()
store.dispatch(action)
}
deleteItem(index) {
// 获取 index
const action = deleteItemAction(index)
store.dispatch(action)
}
// 在组件引入
import {changeInputAction, addItemAction, deleteItemAction} from './store/actionCreators'
changeInputValue(e) {
// 实时获取输入框内容 e.target.value
const action = changeInputAction(e.target.value)
store.dispatch(action)
}
storeChange() {
this.setState(store.getState())
}
clickBtn() {
const action = addItemAction()
store.dispatch(action)
}
deleteItem(index) {
// 获取 index
const action = deleteItemAction(index)
store.dispatch(action)
}
// Action 文件 来管理 action 对象
import { CHANGE_INPUT, ADD_ITEM, DELETE_ITEM } from './actionTypes';
export const changeInputAction = (value) => {
return {
type: CHANGE_INPUT,
value,
};
};
export const addItemAction = () => {
return {
type: ADD_ITEM,
};
};
export const deleteItemAction = (index) => {
return {
type: DELETE_ITEM,
index,
};
};
// Action 文件 来管理 action 对象
import { CHANGE_INPUT, ADD_ITEM, DELETE_ITEM } from './actionTypes';
export const changeInputAction = (value) => {
return {
type: CHANGE_INPUT,
value,
};
};
export const addItemAction = () => {
return {
type: ADD_ITEM,
};
};
export const deleteItemAction = (index) => {
return {
type: DELETE_ITEM,
index,
};
};
Redux 三个小坑
Store 必须是唯一的
在一个文件中用createStore()方法,声明了一个store,之后整个应用都得使用这个store
在一个文件中用createStore()方法,声明了一个store,之后整个应用都得使用这个store
只有 Store 能改变自己的数据内容, Reducer 不能改变
很多小伙伴会认为把业务逻辑写在了Reducer中,那改变state值的一定是Reducer,
其实不然,在Reducer中我们只是作了一个返回,返回到了store中,并没有作任何改变。
Reudcer只是返回了更改的数据,但是并没有更改store中的数据,
store拿到了Reducer的数据,自己对自己进行了更新。
很多小伙伴会认为把业务逻辑写在了Reducer中,那改变state值的一定是Reducer,
其实不然,在Reducer中我们只是作了一个返回,返回到了store中,并没有作任何改变。
Reudcer只是返回了更改的数据,但是并没有更改store中的数据,
store拿到了Reducer的数据,自己对自己进行了更新。
Reducer 必须是纯函数
纯函数的定义:一个函数的返回结果只依赖其参数,并且执行过程中没有副作用
函数执行的过程中对外部产生了可观察的变化,我们就说函数产生了副作用。 例如修改外部的变量、调用 DOM API 修改页面,发送 Ajax 请求、调用 window.reload 刷新浏览器甚至是 console.log 打印数据,都是副作用
永远不要在 reducer 里做这些操作:
- 修改传入参数;
- 执行有副作用的操作,如 API 请求和路由跳转;
- 调用非纯函数,如
Date.now()或Math.random()。
redux 中间件机制
如果不用中间件能不能实现异步? 可以
middleware只是包装了 store 的 dispatch 方法。技术上讲,任何 middleware 能做的事情,都可能通过手动包装 dispatch 调用来实现,但是放在同一个地方统一管理会使整个项目的扩展变的容易得多。
详细介绍:https://cn.redux.js.org/understanding/history-and-design/middleware
在 "Redux 深入浅出" 教程中 你已经学习过在 action 里的 middleware。如果你使用过服务端框架像 Express 或 Koa,你或许已经熟悉 middleware 的概念。在这些框架中,middlewares 可以让你在接收请求和生成响应之间放置的一些代码。例如,Express 或 Koa middleware 可能会添加 CORS 标头、记录日志、压缩等。Middleware 的最大特点是它可以组合成一个链。你可以在一个项目中使用多个不同的独立三方 middlewares。
Redux middleware 解决的问题与 Express 或 Koa middleware 不同,但在概念上是相似的。它在 dispatch action 的时候和 action 到达 reducer 那一刻之间提供了三方的逻辑拓展点。可以使用 Redux middleware 进行日志记录、故障监控上报、与异步 API 通信、路由等。
Redux只是个纯粹的状态管理器,默认只支持同步,实现异步任务 比如延迟,网络请求,需要中间件的支持,比如常见的redux-thunk、redux-saga、redux-logger 、redux-promise等。
Redux 中间件
如果用过 express.js 之类的 web 框架,对中间件(Middleware)这个概念可能不会陌生。中间件其实就是一种独立运行于各个框架组件之间的胶水代码。在 Express.js 或 Koa 等框架中,中间件通常是运行在收到请求到处理请求之间,可是实现日志记录、身份认证等预处理操作。
而在 Redux 里,中间件是运行在 action 发送出去,到达 reducer 之间的一段代码。
redux-thunk 中间件
安装
npm install --save redux-thunk
配置 redux-thunk 中间件
- 如果你没有 Redux DevTools 调试插件 官方提供的配置步骤就是正确的
- 要启用 Redux Thunk,请使用
applyMiddleware()
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import reducer from './reducers/index';
// Note: this API requires redux@>=3.1.0
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import reducer from './reducers/index';
// Note: this API requires redux@>=3.1.0
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
- 如果你之前配置了 Redux DevTools 调试插件
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
- createStore() 函数的第二个参数就是 Redux DevTools 的 配置
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
- 这个时候 官方的配置就没有用了
方法:
如果想两个同时使用,需要使用增强函数。使用增加函数前需要先引入
composeimport { createStore , applyMiddleware ,compose } from 'redux'
然后利用
compose创造一个增强函数,就相当于建立了一个链式函数,代码如下:- js
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__ ? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({}) : compose;const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__ ? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({}) : compose;
有了增强函数后,就可以把
thunk加入进来了,这样两个函数就都会执行了。const enhancer = composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(thunk))
这时候直接在
createStore函数中的第二个参数,使用这个enhancer变量就可以了,相当于两个函数都执行了。const store = createStore( reducer, enhancer) // 创建数据存储仓库
也许对增加函数还不能完全理解,其实你完全把这个想成固定代码,直接使用就好,
全部代码:
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux'; // 引入createStore方法
import reducer from './reducer';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__
? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({})
: compose;
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(thunk));
const store = createStore(reducer, enhancer); // 创建数据存储仓库
export default store; //暴露出去
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux'; // 引入createStore方法
import reducer from './reducer';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__
? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({})
: compose;
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(thunk));
const store = createStore(reducer, enhancer); // 创建数据存储仓库
export default store; //暴露出去
Redux-thunk 基本使用方法
以前
actionCreators.js都是定义好的 action,根本没办法写业务逻辑,有了Redux-thunk之后,可以把TodoList.js中的componentDidMount业务逻辑放到这里来编写。也就是把向后台请求数据的代码放到actionCreators.js文件里。那我们需要引入axios,并写一个新的函数方法。(以前的 action 是对象,现在的 action 可以是函数了,这就是redux-thunk带来的好处)
使用步骤:
- 在 平时创建 action 文件中 写个 action 但是 这次return的是 函数 不是对象
- 函数内部就是用于处理一些异步操作
- 在组件逻辑部分里执行这个 action 后 接收一个返回值 就是 上面的函数。 再 store.dispatch(action) 回去执行 action 函数的代码
举个列子:
// 在 actionCreators 文件中
// 使用 Redux-thunk 后 现在的 action可以是个函数
export const getSongData = () => {
return (dispatch) => {
axios.get('http://120.25.163.140:3000/playlist/hot').then((res) => {
const data = res.data.tags;
console.log(data);
// 最后数据 data 是通过另外一个 action 对象 给 dispatch 回 store
dispatch(songData(data));
});
};
};
export const songData = (song) => {
return {
type: SONG_DATA,
song,
};
};
// 在 reducer.js 文件中
if (action.type === SONG_DATA) {
let newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state)); // 对 state 深度拷贝
newState[action.type] = action.song;
return newState;
}
// 在 actionCreators 文件中
// 使用 Redux-thunk 后 现在的 action可以是个函数
export const getSongData = () => {
return (dispatch) => {
axios.get('http://120.25.163.140:3000/playlist/hot').then((res) => {
const data = res.data.tags;
console.log(data);
// 最后数据 data 是通过另外一个 action 对象 给 dispatch 回 store
dispatch(songData(data));
});
};
};
export const songData = (song) => {
return {
type: SONG_DATA,
song,
};
};
// 在 reducer.js 文件中
if (action.type === SONG_DATA) {
let newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state)); // 对 state 深度拷贝
newState[action.type] = action.song;
return newState;
}
// 在 组件的逻辑文件中 componentDidMount 生命函数里
componentDidMount() {
// 执行 上面的函数 会 return 一个 函数回来 就是这个 action
const action = getSongData()
console.log(action)
// 这里的 store.dispatch(action) 相当于 执行了 action这个函数
store.dispatch(action)
}
// 在 组件的逻辑文件中 componentDidMount 生命函数里
componentDidMount() {
// 执行 上面的函数 会 return 一个 函数回来 就是这个 action
const action = getSongData()
console.log(action)
// 这里的 store.dispatch(action) 相当于 执行了 action这个函数
store.dispatch(action)
}
redux-saga 中间件
安装
cnpm install redux-saga --save
配置 redux-saga 中间件
- 如果没有配置了 Redux DevTools 调试插件
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga'; // +
// redux-saga希望你把业务逻辑单独写一个文件
// 在 sagas文件中 最先基本的配置 (此处必须使用Generator函数)
import helloSaga from './sagas'; // +
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware(); // +
const store = createStore(
reducer,
applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware) // +
);
sagaMiddleware.run(helloSaga); // +
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga'; // +
// redux-saga希望你把业务逻辑单独写一个文件
// 在 sagas文件中 最先基本的配置 (此处必须使用Generator函数)
import helloSaga from './sagas'; // +
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware(); // +
const store = createStore(
reducer,
applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware) // +
);
sagaMiddleware.run(helloSaga); // +
- 如果有配置了 Redux DevTools 调试插件
// 先再 store的index文件中引入 redux-saga
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga'; // +
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux';
import reducer from './reducer';
import todoSagas from './sagas'; // +
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware(); // +
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__
? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({})
: compose;
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware)); // +
const store = createStore(reducer, enhancer);
sagaMiddleware.run(todoSagas); // +
export default store;
// 先再 store的index文件中引入 redux-saga
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga'; // +
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux';
import reducer from './reducer';
import todoSagas from './sagas'; // +
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware(); // +
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__
? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({})
: compose;
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware)); // +
const store = createStore(reducer, enhancer);
sagaMiddleware.run(todoSagas); // +
export default store;
// redux-saga希望你把业务逻辑单独写一个文件
// 在 sagas文件中 最先基本的配置 (此处必须使用Generator函数)
function* mySaga() {}
export default mySaga;
// redux-saga希望你把业务逻辑单独写一个文件
// 在 sagas文件中 最先基本的配置 (此处必须使用Generator函数)
function* mySaga() {}
export default mySaga;
 Attraction11
Attraction11